The Role of the Product of Magnetic Bead Inductor in Practical Applications
I. Introduction
In the realm of electrical engineering, inductors play a crucial role in managing electrical energy. Among the various types of inductors, magnetic bead inductors have gained significant attention due to their unique properties and applications. This blog post will explore the role of the product of magnetic bead inductors in practical applications, shedding light on their structure, working principles, and the significance of their product in circuit design.
II. Understanding Magnetic Bead Inductors
A. Structure and Composition
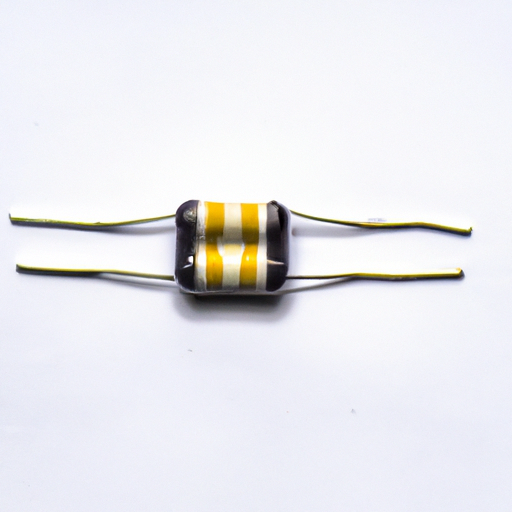
Magnetic bead inductors are compact components typically made from a combination of magnetic materials and conductive wire. The core of these inductors is often composed of ferrite or other magnetic materials that enhance their inductive properties. The design features of magnetic bead inductors include a small form factor, which allows them to be integrated into various electronic devices without occupying significant space.
B. Working Principle
The working principle of magnetic bead inductors is based on electromagnetic induction. When an electric current passes through the inductor, it generates a magnetic field around it. The presence of magnetic beads within the inductor enhances this magnetic field, allowing for greater energy storage and improved inductive performance. This principle is fundamental to the operation of inductors in various applications, from power supplies to communication systems.
III. The Product of Magnetic Bead Inductors
A. Definition of the Product
The product of magnetic bead inductors refers to the combination of two critical parameters: the inductance value and the quality factor (Q). The inductance value indicates the inductor's ability to store energy in the magnetic field, while the quality factor represents the efficiency of the inductor in terms of energy loss. Together, these parameters define the performance characteristics of the inductor in a circuit.
B. Significance of the Product in Circuit Design
In circuit design, the product of magnetic bead inductors is significant for several reasons. First, it aids in impedance matching, ensuring that the inductor can effectively transfer energy between different components in a circuit. Second, it plays a vital role in maintaining signal integrity, particularly in high-frequency applications where signal degradation can occur. A high-quality inductor with an optimal product can minimize losses and enhance overall circuit performance.
IV. Practical Applications of Magnetic Bead Inductors
A. Power Supply Circuits
Magnetic bead inductors are widely used in power supply circuits, where they serve two primary functions: voltage regulation and noise filtering. In voltage regulation, these inductors help maintain a stable output voltage by smoothing out fluctuations in the input voltage. Additionally, they filter out high-frequency noise, ensuring that the power supply delivers clean and reliable energy to connected devices.
B. RF and Communication Systems
In radio frequency (RF) and communication systems, magnetic bead inductors play a crucial role in signal processing and antenna matching. They are used in RF amplifiers to enhance signal strength and clarity, while also ensuring that the impedance of the antenna matches the transmission line. This matching is essential for maximizing signal transmission and minimizing reflections, which can lead to signal loss.
C. Consumer Electronics
Magnetic bead inductors are prevalent in consumer electronics, including audio equipment and mobile devices. In audio applications, they help filter out unwanted noise, ensuring high-quality sound reproduction. In mobile devices, they are used in power management circuits to optimize battery performance and extend battery life.
D. Automotive Applications
The automotive industry has also embraced magnetic bead inductors, particularly in electric vehicles and safety systems. In electric vehicles, these inductors are used in power management systems to regulate energy flow and enhance efficiency. In safety systems, they help filter signals and ensure reliable operation of critical components, such as airbags and anti-lock braking systems.
V. Advantages of Using Magnetic Bead Inductors
Magnetic bead inductors offer several advantages that make them a preferred choice in various applications.
A. Compact Size and Lightweight
One of the most significant benefits of magnetic bead inductors is their compact size and lightweight design. This makes them ideal for modern electronic devices, where space is often at a premium. Their small form factor allows for easy integration into circuit boards without adding unnecessary bulk.
B. High Efficiency
Magnetic bead inductors are known for their high efficiency, particularly in high-frequency applications. Their design minimizes energy losses, ensuring that more energy is stored and transferred effectively. This efficiency is crucial in applications where power conservation is essential, such as in battery-operated devices.
C. Enhanced Performance in High-Frequency Applications
The unique properties of magnetic bead inductors enable them to perform exceptionally well in high-frequency applications. Their ability to maintain signal integrity and minimize losses makes them suitable for RF and communication systems, where signal clarity is paramount.
VI. Challenges and Limitations
Despite their advantages, magnetic bead inductors also face several challenges and limitations.
A. Temperature Sensitivity
Magnetic bead inductors can be sensitive to temperature variations, which can affect their performance. High temperatures may lead to changes in inductance values and quality factors, potentially compromising circuit functionality. Engineers must consider these factors when designing circuits that incorporate magnetic bead inductors.
B. Saturation Effects
Saturation effects can occur when the magnetic core of the inductor reaches its maximum magnetic flux density. When this happens, the inductor's ability to store energy diminishes, leading to reduced performance. Designers must ensure that the inductor operates within its specified limits to avoid saturation.
C. Manufacturing Variability
Manufacturing variability can also impact the performance of magnetic bead inductors. Differences in material properties, production processes, and quality control can lead to variations in inductance values and quality factors. This variability can pose challenges in applications where precise performance is required.
VII. Future Trends and Innovations
As technology continues to evolve, so too do the trends and innovations surrounding magnetic bead inductors.
A. Advances in Material Science
Ongoing research in material science is leading to the development of new magnetic materials that can enhance the performance of magnetic bead inductors. These advancements may result in inductors with improved efficiency, higher inductance values, and better thermal stability.
B. Integration with Other Technologies
The integration of magnetic bead inductors with other technologies, such as digital signal processing and smart materials, is an area of growing interest. This integration could lead to the development of more sophisticated circuits that can adapt to changing conditions and optimize performance in real-time.
C. Potential for Miniaturization
As the demand for smaller and more efficient electronic devices continues to rise, the potential for miniaturization of magnetic bead inductors is significant. Innovations in manufacturing techniques and materials may enable the production of even smaller inductors without compromising performance.
VIII. Conclusion
In conclusion, magnetic bead inductors play a vital role in modern electrical engineering, with their product being a key factor in their performance and application. From power supply circuits to consumer electronics and automotive systems, these inductors are essential for ensuring efficient energy management and signal integrity. As technology advances, the future of magnetic bead inductors looks promising, with ongoing research and innovation paving the way for enhanced performance and new applications. Understanding the role of magnetic bead inductors and their products will be crucial for engineers and designers as they continue to push the boundaries of what is possible in electronic design.
IX. References
1. Academic Journals
2. Industry Reports
3. Technical Manuals and Guides
This blog post provides a comprehensive overview of the role of magnetic bead inductors in practical applications, highlighting their significance, advantages, challenges, and future trends. By understanding these components, engineers and enthusiasts can better appreciate their impact on modern technology.
The Role of the Product of Magnetic Bead Inductor in Practical Applications

I. Introduction
In the realm of electrical engineering, inductors play a crucial role in managing electrical energy. Among the various types of inductors, magnetic bead inductors have gained significant attention due to their unique properties and applications. This blog post will explore the role of the product of magnetic bead inductors in practical applications, shedding light on their structure, working principles, and the significance of their product in circuit design.
II. Understanding Magnetic Bead Inductors
A. Structure and Composition
Magnetic bead inductors are compact components typically made from a combination of magnetic materials and conductive wire. The core of these inductors is often composed of ferrite or other magnetic materials that enhance their inductive properties. The design features of magnetic bead inductors include a small form factor, which allows them to be integrated into various electronic devices without occupying significant space.
B. Working Principle
The working principle of magnetic bead inductors is based on electromagnetic induction. When an electric current passes through the inductor, it generates a magnetic field around it. The presence of magnetic beads within the inductor enhances this magnetic field, allowing for greater energy storage and improved inductive performance. This principle is fundamental to the operation of inductors in various applications, from power supplies to communication systems.
III. The Product of Magnetic Bead Inductors
A. Definition of the Product
The product of magnetic bead inductors refers to the combination of two critical parameters: the inductance value and the quality factor (Q). The inductance value indicates the inductor's ability to store energy in the magnetic field, while the quality factor represents the efficiency of the inductor in terms of energy loss. Together, these parameters define the performance characteristics of the inductor in a circuit.
B. Significance of the Product in Circuit Design
In circuit design, the product of magnetic bead inductors is significant for several reasons. First, it aids in impedance matching, ensuring that the inductor can effectively transfer energy between different components in a circuit. Second, it plays a vital role in maintaining signal integrity, particularly in high-frequency applications where signal degradation can occur. A high-quality inductor with an optimal product can minimize losses and enhance overall circuit performance.
IV. Practical Applications of Magnetic Bead Inductors
A. Power Supply Circuits
Magnetic bead inductors are widely used in power supply circuits, where they serve two primary functions: voltage regulation and noise filtering. In voltage regulation, these inductors help maintain a stable output voltage by smoothing out fluctuations in the input voltage. Additionally, they filter out high-frequency noise, ensuring that the power supply delivers clean and reliable energy to connected devices.
B. RF and Communication Systems
In radio frequency (RF) and communication systems, magnetic bead inductors play a crucial role in signal processing and antenna matching. They are used in RF amplifiers to enhance signal strength and clarity, while also ensuring that the impedance of the antenna matches the transmission line. This matching is essential for maximizing signal transmission and minimizing reflections, which can lead to signal loss.
C. Consumer Electronics
Magnetic bead inductors are prevalent in consumer electronics, including audio equipment and mobile devices. In audio applications, they help filter out unwanted noise, ensuring high-quality sound reproduction. In mobile devices, they are used in power management circuits to optimize battery performance and extend battery life.
D. Automotive Applications
The automotive industry has also embraced magnetic bead inductors, particularly in electric vehicles and safety systems. In electric vehicles, these inductors are used in power management systems to regulate energy flow and enhance efficiency. In safety systems, they help filter signals and ensure reliable operation of critical components, such as airbags and anti-lock braking systems.
V. Advantages of Using Magnetic Bead Inductors
Magnetic bead inductors offer several advantages that make them a preferred choice in various applications.
A. Compact Size and Lightweight
One of the most significant benefits of magnetic bead inductors is their compact size and lightweight design. This makes them ideal for modern electronic devices, where space is often at a premium. Their small form factor allows for easy integration into circuit boards without adding unnecessary bulk.
B. High Efficiency
Magnetic bead inductors are known for their high efficiency, particularly in high-frequency applications. Their design minimizes energy losses, ensuring that more energy is stored and transferred effectively. This efficiency is crucial in applications where power conservation is essential, such as in battery-operated devices.
C. Enhanced Performance in High-Frequency Applications
The unique properties of magnetic bead inductors enable them to perform exceptionally well in high-frequency applications. Their ability to maintain signal integrity and minimize losses makes them suitable for RF and communication systems, where signal clarity is paramount.
VI. Challenges and Limitations
Despite their advantages, magnetic bead inductors also face several challenges and limitations.
A. Temperature Sensitivity
Magnetic bead inductors can be sensitive to temperature variations, which can affect their performance. High temperatures may lead to changes in inductance values and quality factors, potentially compromising circuit functionality. Engineers must consider these factors when designing circuits that incorporate magnetic bead inductors.
B. Saturation Effects
Saturation effects can occur when the magnetic core of the inductor reaches its maximum magnetic flux density. When this happens, the inductor's ability to store energy diminishes, leading to reduced performance. Designers must ensure that the inductor operates within its specified limits to avoid saturation.
C. Manufacturing Variability
Manufacturing variability can also impact the performance of magnetic bead inductors. Differences in material properties, production processes, and quality control can lead to variations in inductance values and quality factors. This variability can pose challenges in applications where precise performance is required.
VII. Future Trends and Innovations
As technology continues to evolve, so too do the trends and innovations surrounding magnetic bead inductors.
A. Advances in Material Science
Ongoing research in material science is leading to the development of new magnetic materials that can enhance the performance of magnetic bead inductors. These advancements may result in inductors with improved efficiency, higher inductance values, and better thermal stability.
B. Integration with Other Technologies
The integration of magnetic bead inductors with other technologies, such as digital signal processing and smart materials, is an area of growing interest. This integration could lead to the development of more sophisticated circuits that can adapt to changing conditions and optimize performance in real-time.
C. Potential for Miniaturization
As the demand for smaller and more efficient electronic devices continues to rise, the potential for miniaturization of magnetic bead inductors is significant. Innovations in manufacturing techniques and materials may enable the production of even smaller inductors without compromising performance.
VIII. Conclusion
In conclusion, magnetic bead inductors play a vital role in modern electrical engineering, with their product being a key factor in their performance and application. From power supply circuits to consumer electronics and automotive systems, these inductors are essential for ensuring efficient energy management and signal integrity. As technology advances, the future of magnetic bead inductors looks promising, with ongoing research and innovation paving the way for enhanced performance and new applications. Understanding the role of magnetic bead inductors and their products will be crucial for engineers and designers as they continue to push the boundaries of what is possible in electronic design.
IX. References
1. Academic Journals
2. Industry Reports
3. Technical Manuals and Guides
This blog post provides a comprehensive overview of the role of magnetic bead inductors in practical applications, highlighting their significance, advantages, challenges, and future trends. By understanding these components, engineers and enthusiasts can better appreciate their impact on modern technology.






